This appendix to our Annual Risk Report gives further statistics on incident information and telemetry detailing the instruments utilized by cybercriminals concentrating on small and midsized companies (SMBs). For a broader have a look at the menace panorama dealing with SMBs, see our principal report.
Appendix Contents:
Most often-encountered malware sorts
Small and midsized companies face an unlimited set of threats to information—a few of which can be precursors to ransomware assaults or could end in different breaches of delicate data. Ransomware dominates the malware noticed in Sophos MDR and Sophos Incident Response circumstances from 2024, with the highest 10 accounting for over 25% of all incidents MDR and IR tracked over the yr. However they weren’t the whole story, and almost 60% of MDR incidents concerned threats not involving ransomware.
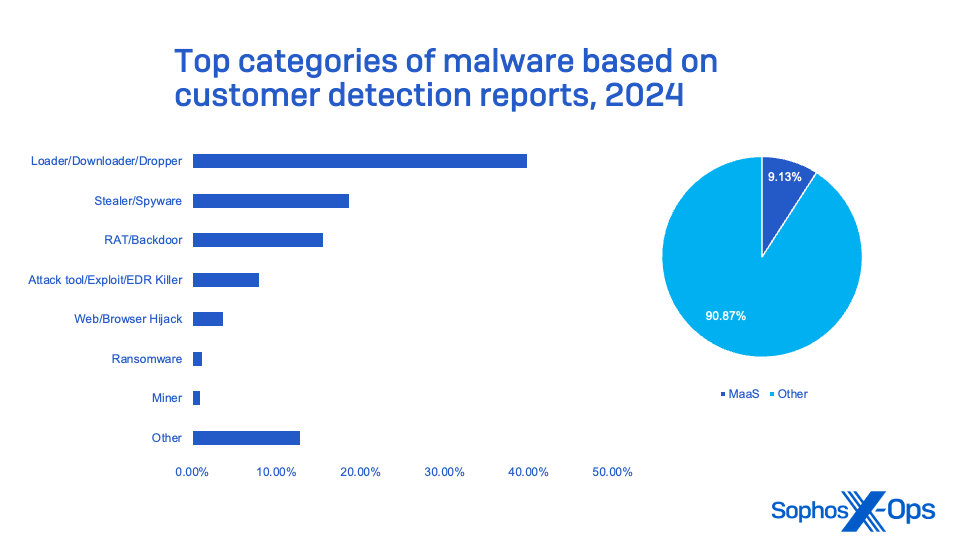
Determine 13: Probably the most generally seen classes of malware detection seen in 2024, based mostly on buyer detection stories
Command-and-control instruments, malware loaders, distant administration instruments, and information-stealing malware make up the vast majority of the malicious software program seen concentrating on small companies (other than ransomware). And these instruments, not all of that are technically malware, are used as a part of the supply of ransomware and different cybercriminal assaults.
Solely one of many high 10 instruments and malware seen in Sophos MDR and IR incidents doesn’t fall into this class: XMRig. It’s a cryptocurrency-mining malware typically used to passively generate income earlier than entry is offered or in any other case exploited by a ransomware actor.


Twin-use instruments
One development that continues from earlier years is the in depth use of usually accessible industrial, freeware, and open-source software program by cybercriminals to conduct ransomware assaults and different malicious exercise. Sophos MDR refers to those as “dual-use instruments,” as they might be current on networks for reliable causes, however are continuously utilized by cybercriminals for malicious functions.
Twin-use instruments are totally different from “living-off-the-land binaries” (LOLBins) in that they’re full purposes deployed and used as meant by malicious actors, moderately than working system-supplied parts and scripting engines. Among the instruments that fall into “twin use” are particularly safety testing-oriented and meant for crimson groups—Impacket and Mimikatz are open-source instruments that have been constructed particularly for safety researchers. Others akin to SoftPerfect Community Scanner and Superior IP Scanner are meant as instruments for community directors, however can be utilized by cybercriminals for discovery of networked gadgets and open community ports.
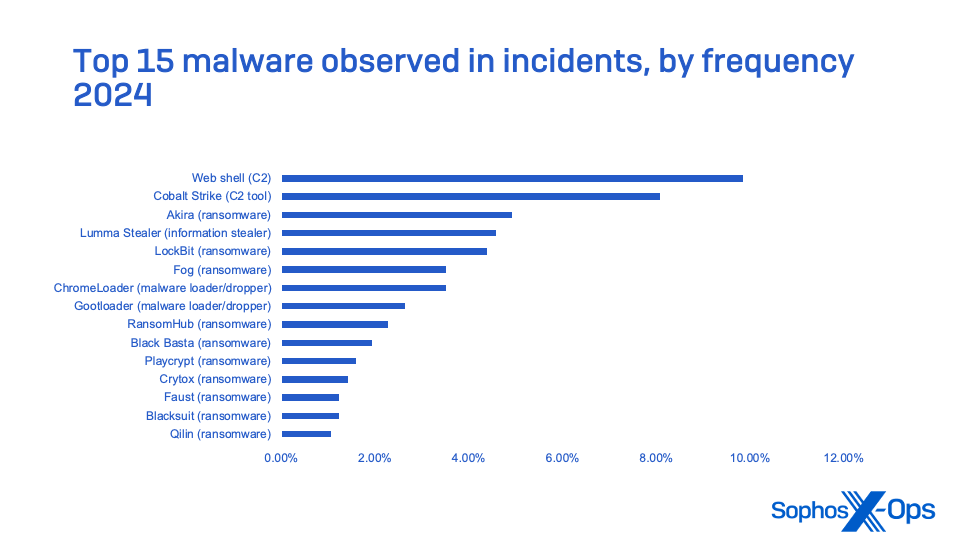
Determine 17: High 15 “twin use” instruments seen in Sophos MDR and Sophos Incident Response incidents, by frequency
Determine 18: High 9 “twin use” assault instruments in Sophos endpoint detections
Industrial distant entry instruments are collectively probably the most continuously used dual-use instruments encountered in MDR and IR incidents:

With industrial distant entry instruments, the attackers often abuse trial account licenses or use pirated licenses for the variations they deploy to focused machines. In lots of circumstances, that is achieved after preliminary exploitation by means of malware droppers, internet shells, or different command-and-control instruments. In others, it’s pushed by means of social engineering—getting a focused particular person to obtain and set up the software themselves, as we now have seen in current Groups “vishing” assaults.
Use of reliable distant machine administration instruments, significantly by ransomware actors, has been rising, although distant desktop entry instruments AnyDesk and ScreenConnect stay probably the most continuously used industrial IT help instruments seen in Sophos MDR and IR incidents. And the most typical software stays PSExec, a Microsoft “light-weight Telnet replacement” used to remotely execute instructions and create command shell classes.
Sophos prospects can prohibit their utilization by means of Sophos Central utilizing software management insurance policies—and may prohibit any instruments that aren’t getting used for reliable IT help.
Assault instruments
Cobalt Strike, Sliver, Metasploit, and Brute Ratel are penetration testing instruments, and never malware within the authorized sense. However they’re continuously used to ship malware and for command and management of malware assaults. Having a well-documented, commercially supported post-exploitation software like these is a serious plus for cybercriminals who would in any other case need to construct their very own instruments to increase their footprint inside a focused group.
Cobalt Strike stays probably the most closely used of those assault instruments, current in eight p.c of all incidents and almost 11 p.c of ransomware-related incidents. It is a vital decline from 2023, when Cobalt Strike was the third most continuously seen industrial software utilized in MDR incidents, rating solely behind the AnyDesk and PSExec distant entry instruments. Sliver and Metasploit-based instruments, which can be found as open-source, are seen even much less continuously, and Brute Ratel utilization by cybercriminals stays extraordinarily uncommon.
Info stealers

Info-stealing malware is commonly step one within the entry dealer’s playbook, offering passwords, cookies, and different information that can be utilized for monetary fraud, enterprise e-mail compromise, and ransomware assaults, amongst different schemes.
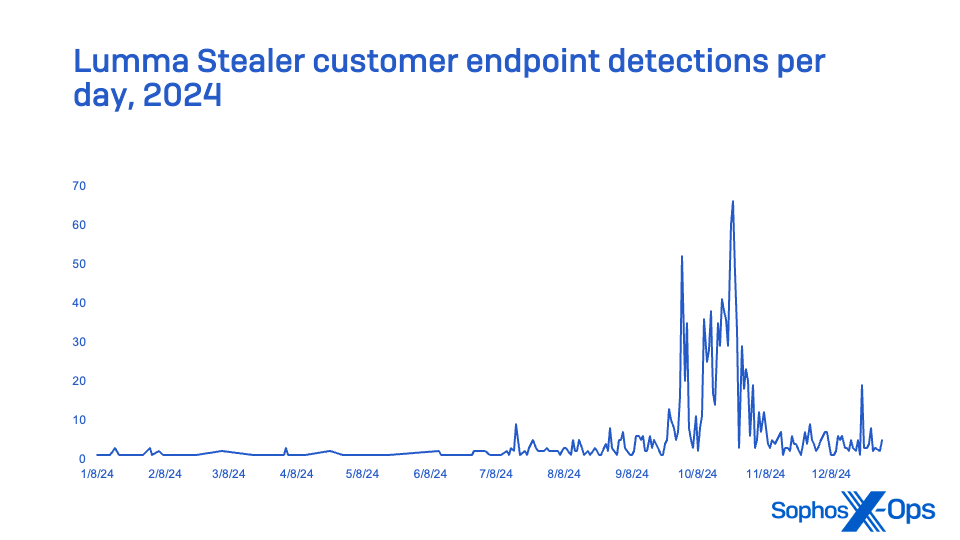
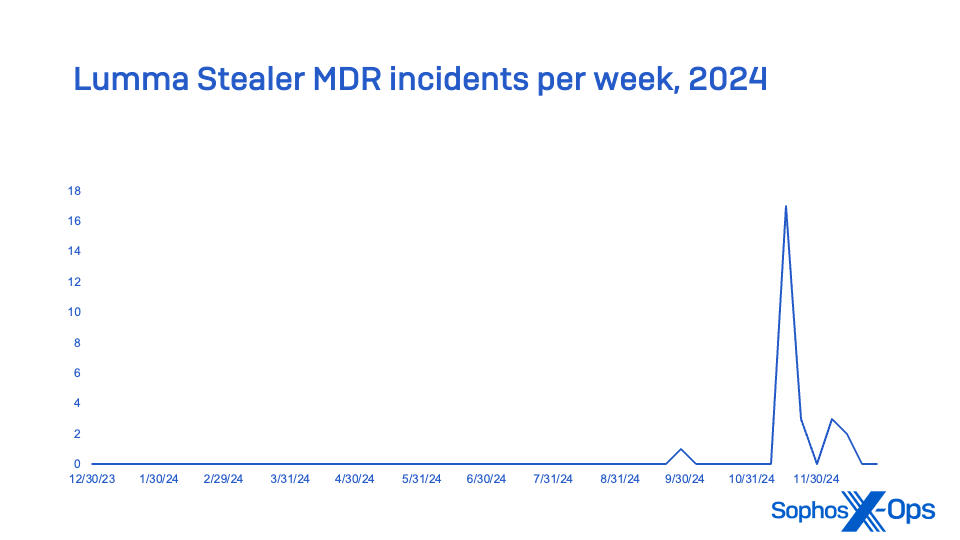
Lumma Stealer, offered by means of Russian-speaking boards as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), was probably the most continuously encountered data stealer in MDR incidents, and second in total endpoint detection stories. A significant Lumma Stealer marketing campaign starting in October made it probably the most reported stealer for the final quarter of 2024, far surpassing final yr’s MaaS stealer chief RaccoonStealer (which launched a brand new model in 2024 after its infrastructure was disrupted) and by yr’s finish eclipsing Strela Stealer (which was rising within the ranks in 2023; it peaked early in 2024, however trailed off within the second half of the yr). No MDR incidents tracked in 2024 concerned Strela Stealer.
Determine 21: Lumma Stealer exercise in 2024 as noticed in buyer endpoint detections

First tracked in August 2022, Lumma Stealer is believed to be a successor of Mars Stealer, one other data stealer purportedly of Russian origin. This stealer primarily targets cryptocurrency wallets, browser session cookies, browser two-factor authentication extensions, saved File Switch Protocol server addresses and credentials, and different consumer and system information.
Like another data stealers (akin to Raccoon Stealer), Lumma Stealer can be used to ship further malware—both by launching executables or PowerShell scripts, or by loading malicious DLLs from its personal course of. Sometimes, Lumma Stealer is delivered from a compromised web site (typically a faux CAPTCHA internet web page) as a obtain that victims are dropped at through malvertising.
Lumma Stealer is mostly related to broader cybercriminal exercise. One other MaaS stealer offered on Russian-language boards, StealC, was seen with a a lot increased correlation to ransomware incidents. Launched in January 2023, it has been labeled by researchers as a RaccoonStealer and Vidar copycat.
Of regional be aware is Mispadu Stealer, which continues to focus on Latin America (and Mexico specifically). Within the second quarter of 2024, it was the second-most detected stealer, coming in simply behind Strela Stealer, with 74% of these detections coming from Mexico. It has been seen utilizing malicious internet and search promoting, notably posing as internet advertisements for McDonald’s.
High ransomware threats


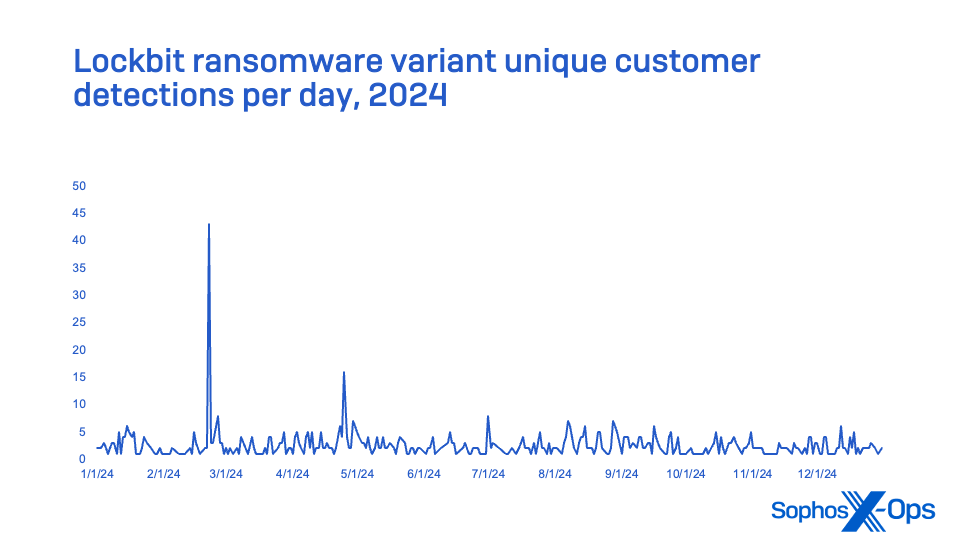
LockBit, kind of
Probably the most-detected ransomware household in 2024 was LockBit, however not due to the ransomware group that spawned it. In February 2024, US and UK legislation enforcement claimed to have disrupted the LockBit group by seizing the ransomware-as-a-service group’s servers, arresting two of its members, and charging one other in an indictment. Within the wake of this disruption, quite a few variants based mostly on the leaked LockBit 3.0 code grew to become lively within the wild, leading to a spike of LockBit detections in early 2024. Nonetheless, by March, detections trailed off considerably with a slight rebound in April and early Could (although the LockBit gang might not be gone endlessly).
The teams utilizing LockBit 3.0 continuously used EDR killers and different malware and strategies to try to disable endpoint safety. Their preliminary entry was typically by means of VPN accounts that had been compromised (in some circumstances resulting from vulnerabilities within the VPN gadgets themselves), or by means of the abuse of credentials harvested from unmanaged gadgets to achieve distant entry.
Akira and Fog
By way of precise incidents, the Akira ransomware-as-a-service led the pack in 2024, finally stepping in to fill the void left by LockBit. Initially seen in 2022, Akira assaults ramped up in late 2023. The group and its associates have been steadily lively all through 2024, spiking in August when Akira accounted for 17% of the ransomware detections reported by Sophos prospects—doubling from its place within the first two quarters of the yr. By yr’s finish, it nonetheless accounted for 9% of ransomware detection stories.
Notably, Sophos noticed associates tied to Akira additionally deploying different ransomware variants, together with Fog, Frag and Megazord. These attackers (akin to these in STAC5881) usually centered on exploiting VPNs for preliminary entry. Sometimes, Akira’s targets had VPNs with no multifactor authentication, or had misconfigured VPN gateways that allowed the attackers to achieve entry with stolen credentials or brute drive assaults.
Whereas Akira stays lively, Fog ransomware has often been used as a substitute by associates beforehand related to Akira, which accounts for its place in third among the many high 15 ransomware households encountered in MDR and IR incidents.
RansomHub
RansomHub was one other rising chief in ransomware incidents in 2024. Whereas tied for sixth in total detections, RansomHub was the fourth most noticed ransomware household in precise MDR and IR incidents.
Between February and August 2024, in line with a Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company #StopRansomware advisory, RansomHub had “encrypted and exfiltrated information from no less than 210 victims.” The vast majority of Sophos MDR and IR circumstances involving RansomHub got here within the second half of the yr, mounting in numbers in November.
Most RansomHub assaults concerned abuse of RDP along with different reliable distant desktop instruments, together with AnyDesk. Preliminary entry in some reported circumstances got here from leveraging the seven-year-old Home windows SMB Distant Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2017-1444), although this was not noticed within the Sophos MDR and IR circumstances represented in our information. Preliminary entry vectors Sophos X-Ops noticed in RansomHub circumstances included abuse of externally dealing with Microsoft SQL Servers for command execution, abuse of open RDP and Distant Desktop Internet entry, and compromise of unmanaged gadgets.