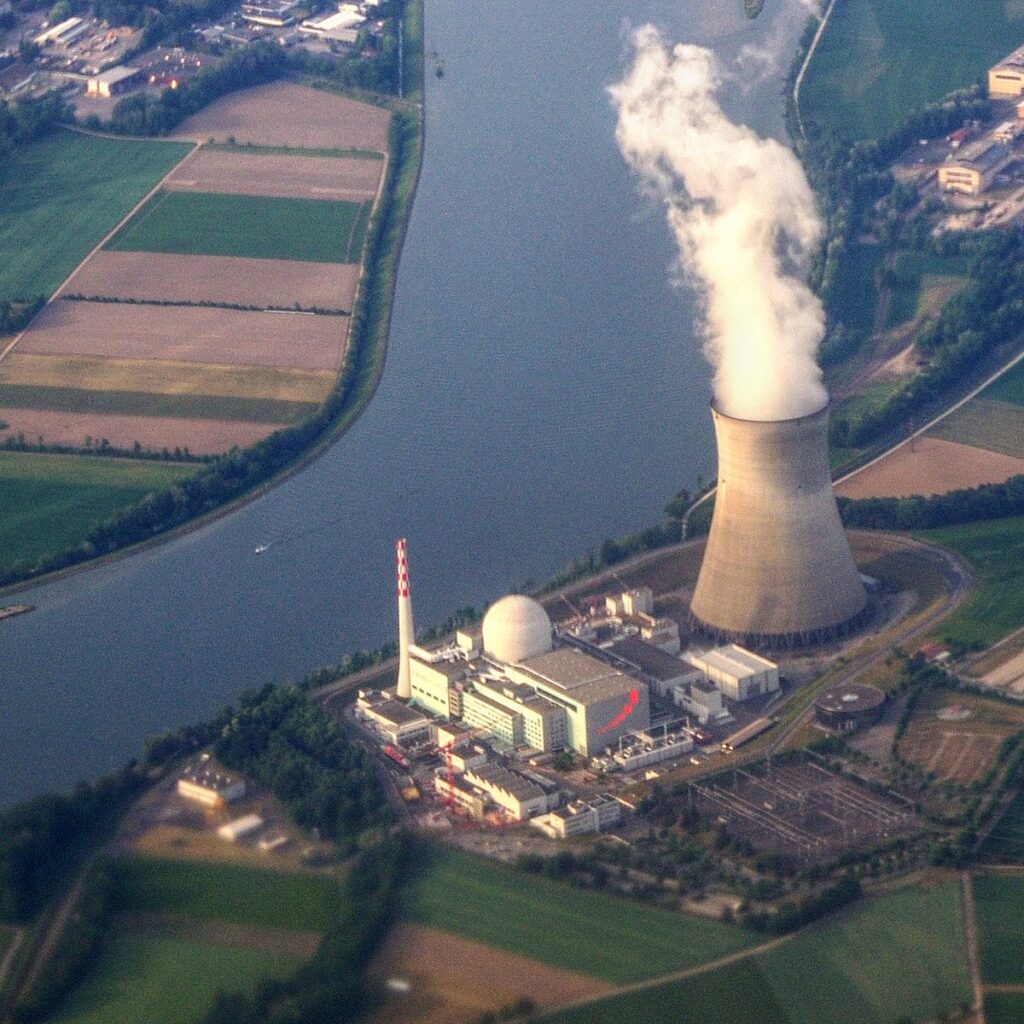
Credit score: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en
Even because the HPC-AI sector cheers on extra highly effective chips, denser servers, quicker materials, larger reminiscence and mammoth, multi-hundreds of billion-dollar AI information facilities, a voice is whispering within the business’s ear: “The place’s the electrical energy for all this?”
Good level! It’s usually assumed the info middle power hole will probably be stuffed by some mixture of extra environment friendly techniques and extra methods of producing better energy. Together with fossil fuels, the main target is on new, ideally clear, power sources, a mixture of photo voltaic, wind, hydrogen and, perhaps sometime, fusion.
Relating to nuclear energy, Deloitte Insights has launched a report, with combined conclusions.
The excellent news – good, that’s, in case you’re not essentially against nuclear power – is that it’s present process a revival and it’s nearly carbon-free. Alternatively, it’s going to at greatest solely partially shut the power hole.
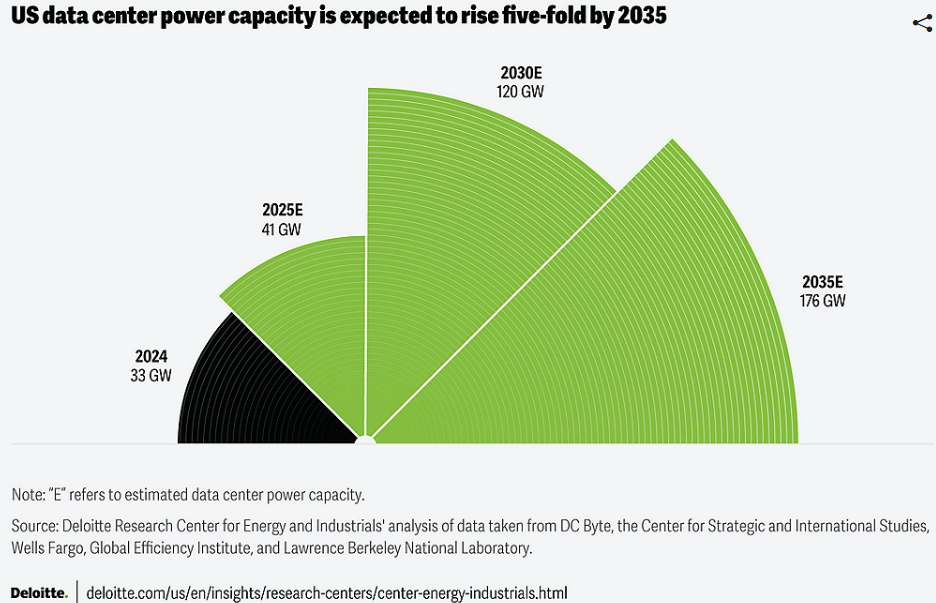
In keeping with Deloitte’s report, information middle electrical energy demand might rise five-fold by 2035, to 176 GW, and the agency stated nuclear energy capability “might doubtlessly meet about 10 % of the projected enhance in information middle energy demand over the subsequent decade. This estimate is predicated on a major enlargement of nuclear capability, ranging between 35 gigawatts and 62 GW throughout the identical interval.”
Presently, nuclear power powers almost 20 % of U.S. electrical energy regardless of representing lower than 8 % of the nation’s whole working capability. Nonetheless, the nation’s nuclear useful resource is getting older: the U.S. has 94 working reactors with a median age of 42 years.
Deloitte Insights reported that greater than 80 % of those reactors have been relicensed to function for as much as 60 years and even 80 years with a subsequent license renewal. Upgrades and modernization of those reactors might increase capability. Deloitte cited sources reporting that “The cumulative uprates from 1977 to 2021 quantity to eight,030 MW, averaging about 0.18 GW per yr over 44 years.”
As well as, reviving closed vegetation, as Microsoft intends to do with the previous Three Mile Island plant in Pennsylvania, is an alternative choice that’s inexpensive than constructing new vegetation of comparable capability, Deloitte stated.
Different tasks name for constructing new reactors at present nuclear and coal-fired energy websites, “profiting from present infrastructure and streamlined licensing processes.”
One other strategy is small modular reactors (SMRs). These factory-built reactors supply potential advances over conventional nuclear reactors, Deloitte stated, together with “black begin functionality, islanding, underground development, gas safety, and steady operation, making them extremely resilient and appropriate for infrastructure like information facilities.”
Relating to next-generation reactor designs Deloitte stated they’ve the potential to “improve security, effectivity, and gas utilization, and microreactors supply distinctive benefits for distant areas, off-grid functions, and specialised power wants, making them viable choices for powering information facilities.”
As well as, SMRs “drastically cut back development timelines” and might improve security, incorporating “passive security techniques (gravity, pure circulation), doubtlessly decreasing the necessity for operator intervention. The smaller core and decrease energy density additional reduce dangers. Some designs even incorporate underground development for added safety.”
Nonetheless, nuclear energy stays a controversial power supply. As Deloitte acknowledged, “public opinion on nuclear energy in the US is complicated and evolving, and so the trail to scaling it for information middle demand will not be with out challenges.”
As well as, nuclear vegetation usually face prolonged regulatory approval cycles and “typically face challenges associated to development timelines and price overruns, which might hinder their financial viability and competitiveness with different power sources,” Deloitte reported, citing a commercialized undertaking that went over price range by greater than 114 % and was delayed six years.
Nuclear energy plant development is dear. Deloitte cited a supply reporting that “In 2024, the capital expenditure to develop nuclear services ranged from US$6,417 to US$12,681 per kilowatt (kW), whereas that of pure gasoline services was about US$1,290 per kW.”
On the upside, nuclear affords dependable baseload energy, working 24/7 no matter climate circumstances, in contrast to wind and photo voltaic. Nuclear additionally has the next capability manufacturing facility than pure gasoline, 92.5 % vs. 56 %.
And nuclear is scalable. Deloitte’s report acknowledged that “a single nuclear reactor usually generates 800 megawatts (MW) or extra of electrical energy, readily assembly the facility calls for of even the biggest information facilities (50 MW to 100 MW) and the burgeoning necessities of AI-focused services (as much as 5,000 MW).”
In all, nuclear affords promise, perils and a partial answer for the power hole.
The total report will be discovered right here.














