Underground warmth will increase as we go deeper into the Earth, providing an nearly limitless vitality supply alongside different renewable options. In some areas of the Earth’s crust, resembling Iceland—the place geothermal wells are a typical vitality supply—excessive temperatures are reached at depths of lower than one kilometre. This warmth generates steam, which can be utilized for heating techniques or to drive generators.
Nonetheless, excessive temperatures will not be crucial for a home geothermal system designed to take care of a snug indoor temperature year-round. One firm is now exploring the potential of shallow boreholes with a conveyable tunnelling machine that can be utilized nearly wherever—from a storage to a yard.
What are geothermal wells?
A geothermal effectively is a borehole designed to harness the Earth’s pure warmth for energy technology or local weather management. Sometimes, these boreholes prolong to underground layers the place temperatures are larger, capturing geothermal vitality to supply electrical energy, heating, or cooling in a sustainable manner.
When it comes to depth, geothermal wells can fluctuate vastly—from shallow warmth trade techniques with boreholes only some metres deep to wells that attain a number of kilometres for high-enthalpy installations, the place warmth and stress generate steam to drive a turbine.
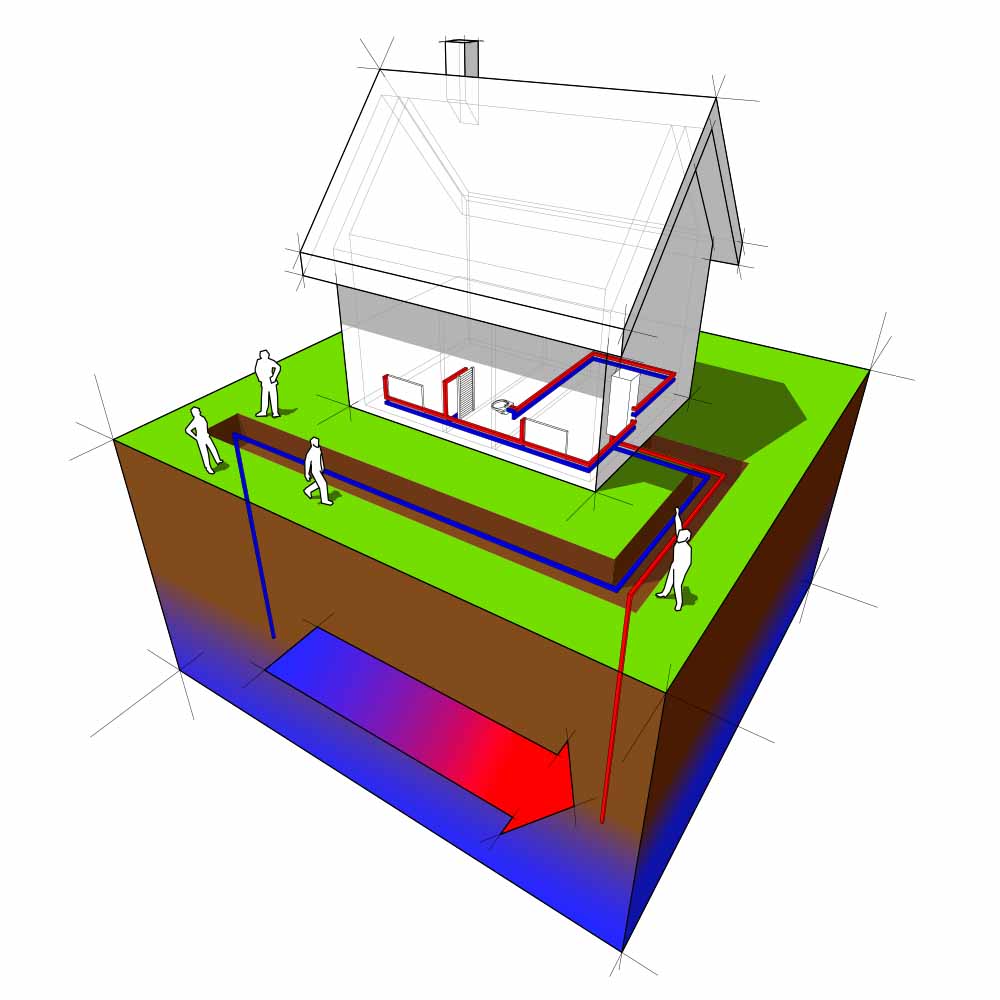
Commonest forms of geothermal wells:
1. Shallow or low-enthalpy wells
- Primarily used for heating and cooling buildings through warmth pumps.
- Sometimes drilled to depths of some dozen metres.
2. Medium-enthalpy wells
- Preferrred for industrial processes and district heating.
- Attain depths of a number of hundred metres.
3. Excessive enthalpy wells
- Can prolong between 1,000 and three,000 metres (or extra).
- Used for large-scale electrical energy manufacturing by extracting steam and high-temperature geothermal fluids.
A mini-tunneling machine in your backyard
Should you observe our web site, you could have come throughout our discussions on tunnel boring machines (TBMs)—the huge steel worms that carve by means of the earth to create tunnels for autos and passengers, such because the Quito Metro or São Paulo’s Line 6. These machines can weigh as much as 5,000 tonnes and require complicated operations, usually that includes a reducing head, a propulsion system, and onboard personnel to regulate them.
Swiss firm Borobotics has taken a special method, creating a miniature tunnel boring machine for geothermal exploration. Whereas its design is much like typical TBMs, the variations are substantial. The machine, named Grabowski after the cartoon mole, is lower than 14 centimetres in diameter and solely 2.8 metres lengthy. Furthermore, its “worm” is autonomous and requires lower than eight sq. metres of area to function. In actual fact, each the worm and its floor tools match right into a small van, and a single operator is sufficient to deal with the set up.
Powered by an electrical propulsion system, the system options sensors that detect the kind of materials it’s drilling by means of and robotically cease if it encounters a water or fuel deposit, which it might additionally seal by itself. Moreover, it might regulate its course because it drills, following the trail of least resistance. It’s able to boring by means of varied floor sorts, from sand to granite.
Based on its creators, Grabowski can attain depths of as much as 500 metres—nonetheless removed from typical geothermal wells however greater than ample to stabilise a house’s temperature. They notice that at a depth of 250 metres, the common temperature is round 14°C. Geothermal warmth pumps flow into air to chill buildings in summer time and heat them in winter relative to the out of doors temperature.
Should you’re excited about different modern renewable vitality options past geothermal wells and solar energy, try our articles on the triboelectric impact and wave vitality.
Supply:













